What Is High & Low Pressure Die Casting – Differences Between HPDC Vs LPDC| Diecasting-Mould
In this guide, we present a brief overview of high and low pressure die casting, you can find out how they work and what are differences between them. `
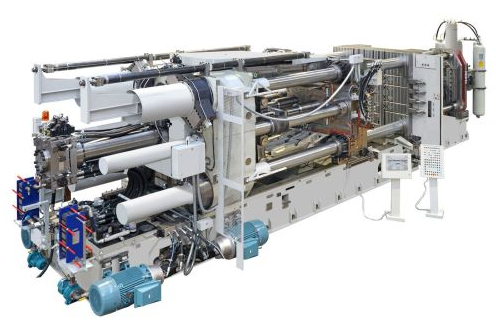
What Is High Pressure Die Casting
High pressure die casting or HPDC is a casting method used to produce metal parts for a variety of industries. For example, engine blocks and gearboxes for automobiles may be cast using HPDC processes though most commonly applied to aluminum alloys HPDC may be used to cast other non-ferrous metals such as brass, zinc or magnesium alloys. The defining trait of HPDC is that high-pressure air is used to force molten metal into a mold cavity. HPDC is considered a permanent mold casting process since the molds that make the castings are permanent and can be reused for many cycles.
Permanent molds are also referred to as dyes. In contrast to permanent molds, destructible molds are broken up to retrieve the castings, these molds include bonded sand molds, molds made from ceramics or similar materials. High pressure die casting foundries typically require several pieces of equipment for each step in the process.
– The melting furnace is required to melt the charged materials and bring the molten metal to the required temperature.
– The molten metal is then typically poured into a transfer ladle which can be moved around the foundry as required.
– After degassing and other processing, the metal is poured into a holding furnace, the holding furnace maintains the molten metal at casting temperatures near the HPDC machine.
– Most modern HP DC foundries use automated or robotic pouring systems. A precise amount of molten metal is scooped in a poor cup and move to the Machine.
– The molten metal is poured into what is referred to as a shot sleeve driven by air pressure. A plunger forces the molten metal through the shot sleeve and up into the closed molds. The metal is allowed to cool and solidify in required casting shape.
– The casting is ejected after solidification and moved on for further processing for the best performance and consistency. Almost all HPDC machines are controlled by a programmable logic controller or PLC.
What Is Low Pressure Die Casting
Low pressure die casting or LPDC is a casting method used to produce metal parts that are typically symmetrical in shape and design. For example, wheel rims and steering knuckles for automobiles may be cast using LPDC processes. Though most commonly applied to aluminum alloys, LPDC may be used to cast other non-ferrous metals such as brass, zinc or magnesium alloys.
In this process, the holding furnace is located below the cast and the liquid metal is forced upwards through a riser tube and into the cavity. The pressure is applied constantly, sometimes in increasing increments, to fill the mold and hold the metal in place within the die until it solidifies. Once the cast has solidified, the pressure is released and any residual liquid in the tube or cavity flows back into the holding furnace for “recycling.” When cooled, the cast is simply removed.

