Aluminum Die Casting Alloy Composition & Properties – What is Die Cast Aluminum | Diecasting-mould
The majority of die castings are made from aluminum alloys, there are lots of different alloys used for aluminum die casting. Here we’ll start with what is die cast aluminum, then go through the common aluminum die casting alloys, including A380, A360, 383, etc., and their composition, properties, to find the best aluminum alloy for die casting.

What is Die Cast Aluminum?
Die cast aluminum is a type of aluminum that is melted to a liquid and forced into the mold cavities under high pressure and then hardens to the desired shape for producing the final die casting aluminum parts. Aluminum die casting uses the non-expendable mold to produce metal castings repeatedly, the die cast aluminum can be fabricated to different dimensions and shapes for a variety of industries, aluminum castings with great accuracy and properties are commonly used in the automotive industry.
Types of Common Aluminum Die Casting Alloys – Best Aluminum Alloy for Die Casting
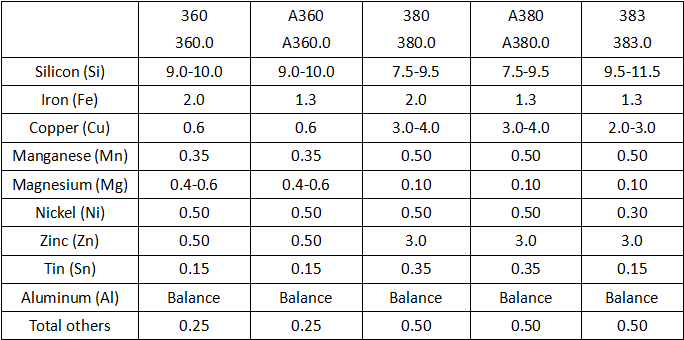
Die cast aluminum alloy mainly consists of silicon, copper, magnesium, iron, manganese, and zinc. Each element has a different impact on the properties of the alloy. When working with aluminum, you need to choose which type of aluminum alloy to use in the die casting services. Looking at the following die casting aluminum alloys to find the best one for yourself.
- Aluminum Alloy A360 (ANSI/AA A360.0): high corrosion resistance, superior strength at elevated temperatures and good ductility, excellent pressure tightness, and high fluidity, but relatively difficult to cast.
- Aluminum Alloy A380 (ANSI/AA A380.0): the most common die cast aluminum, it offers both great properties and ease of production, this alloy exhibits excellent fluidity, light weight, resistance to corrosion and hot cracking, pressure tightness, dimensional stability, high strength at high temperatures and high electrical conductivity, widely used in tools, frames, electronics, communications equipment, automotive engine, and other parts, transmission and gear cases, furniture, appliances, and more industries. Alloy A380 also has better than average machining characteristics.
- Aluminum Alloy 383 (ANSI/AA 383.0): can be used as the alternative of A380 for intricate components, it has good mechanical properties and improved die casting properties.
When it comes to the selection of the best aluminum alloy for die casting, other die casting aluminum alloys including AA C443.0, AA A413.0, AA B390.0, AA 518.0, and more. The most popular alloy for aluminum die casting is A380, you can use A383 when producing intricate die casting components that requiring specific die-filling performance, but the castings made from A383 is not as durable as A380. A360 is more difficult to cast than A380, you can check its properties below when considering using it.
Die Cast Aluminum Material Properties
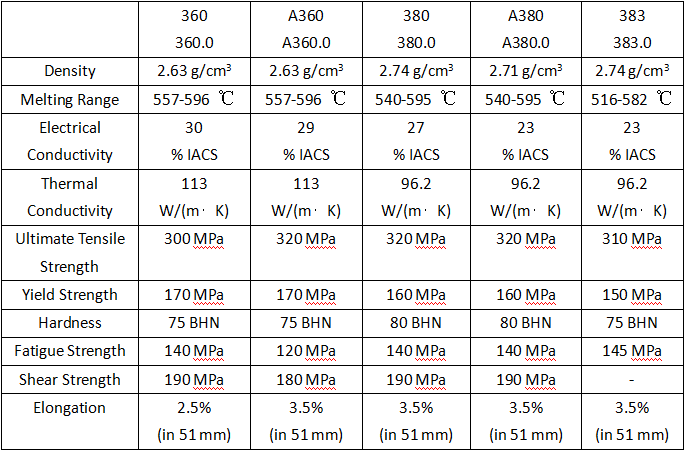
Density: About 2.7 g/cm3, which is roughly one-third the density of steel. This makes it a lightweight yet strong material.
Tensile Strength: 200-350 MPa for common alloys like A380, A360, depending on specific composition and heat treatment. Slightly lower than mild steel but still robust.
Hardness: Range from 30-150 HB depending on alloy and process. Commonly 75-90 HB for general purpose alloys. Heat treatments improve hardness.
Corrosion Resistance: Exhibits excellent corrosion resistance due to a thin, tough oxide layer that forms on the surface and protects the metal. Good for outdoor applications.
Ductility: Typically 5-15% elongation is possible. Certain alloys can achieve 20-30% elongation. More rigid than steels but still has some flexibility.
Heat Conductivity: Significantly lower than steel at around 100-180 W/mK. Good for applications needing heat resistance.
Machinability: More difficult to machine than steel but finishes provide a smooth surface. Machining leaves swarf that needs extraction.
Dimensions: Die casting allows dimensions to be held within a few thousandths of an inch, with complex internal passages.
Cost: Generally cheaper than machining other metals into comparable components. Rapid production process.
Comparison Between Different Aluminum Die Casting Alloys
Here are two comparison tables of aluminum alloy die casting, the first one indicates the chemical composition of different aluminum die cast alloys. The single values listed below refer to the maximum composition percentages. And in the second comparison chart, you can find varying mechanical and physical properties of common cast aluminum alloys.
Aluminum Die Casting Alloy Composition Chart
Aluminum Die Casting Alloy Properties Chart
Is Die Cast Aluminum Safe?
Yes, Die cast aluminum is a material made by melting aluminum alloy and applying pressure through a die casting machine. Under normal circumstances, die cast aluminum material itself has no direct toxicity. It is a silver white light metal with ductility and can form an oxide film to prevent metal corrosion in humid air.
However, during the production process of die cast aluminum, a large amount of gas may be generated. If these gases are inhaled by the human body for a long time, they may have a certain impact on human health. Therefore, workers engaged in die-casting aluminum production need to pay special attention to protective measures to reduce potential health risks.
How Strong is Die Casting Aluminum?
According to ASTM B557 standard, the tensile strength of typical die cast aluminum alloy specimens at room temperature can reach 310-340MPa, yield strength 260-280MPa, and elongation of 3% -5%. High temperature performance testing shows that when the temperature rises to 150 ℃, its strength retention rate is still above 85%, thanks to the stable second phase strengthening effect. The rotational bending fatigue test data shows that the fatigue life of the shot peened sample can reach more than 1 × 10 ^ 7 times under a stress amplitude of 150 MPa.
Generally speaking, die cast aluminum alloys have high tensile strength and good ductility. The strength of die cast aluminum is closely related to its alloy composition, die casting process parameters, and subsequent heat treatment methods.
1. The influence of alloy composition on strength: Other metal elements added to aluminum alloys, such as copper, magnesium, etc., can effectively improve the strength and hardness of the alloy. For example, aluminum copper alloys (such as 2024 alloy) are widely used in the aerospace industry due to their high strength and good processability.
2. The influence of die casting process on strength: Parameters such as pressure, temperature, and time during the die casting process can affect the internal structure and density of die cast aluminum, thereby affecting its strength. High pressure and appropriate temperature can better fill the mold with aluminum liquid, reduce defects such as porosity and shrinkage, and improve the density and strength of the product.
3. The effect of subsequent heat treatment on strength: Heat treatment, such as annealing, aging, etc., can improve the strength and hardness of die cast aluminum alloys by changing their internal microstructure. For example, T6 heat treatment (solution treatment and artificial aging) can significantly improve the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys.
Can You Weld Die Cast Aluminum?
The answer is yes, cast aluminum can indeed be welded. However, we need to understand that welding cast aluminum is not a simple task. This is mainly due to the good thermal conductivity and low melting point of cast aluminum, which makes it prone to deformation during the welding process. Therefore, when welding die cast aluminum alloys, the following points should be noted:
1. Before welding, the cast aluminum parts should be cleaned to remove impurities such as oil stains and oxides on the surface, in order to improve the welding quality.
2. Choose appropriate welding methods and welding materials to ensure that the strength and corrosion resistance of the weld meet the requirements.
3. Control the temperature and speed during the welding process to avoid excessive heat input that may cause deformation or cracking of the cast aluminum parts.
Does Die Cast Aluminum Rust?
can’t. Die cast aluminum is an aluminum alloy material formed by high temperature and high pressure molding, with a dense layer of aluminum oxide film formed on its surface. This film can prevent further oxidation of the aluminum inside, thus having good corrosion resistance. Therefore, die cast aluminum is not easy to rust. However, if the surface of die cast aluminum products is scratched, damaged, or damaged, causing damage to the aluminum oxide film and exposing the aluminum to air, oxidation reactions may occur and rust may occur.
Die Cast Aluminum vs Stainless Steel, What are the Differences?
1. Material composition
Die cast aluminum is an aluminum alloy material mainly composed of metal elements such as aluminum, copper, and zinc, which has high strength and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel is mainly composed of metal elements such as iron, chromium, and nickel, and has excellent corrosion resistance and high strength.
2. Physical properties
Die cast aluminum and stainless steel also have significant differences in physical properties. The density of die cast aluminum is relatively low, about 2.7g/cm ³, with a high coefficient of thermal expansion and good thermal conductivity. Stainless steel has a higher density of about 7.93g/cm ³, a lower coefficient of expansion, and poorer thermal conductivity.
3. Processing technology
Due to its high fluidity and plasticity, die cast aluminum is more flexible in processing technology than stainless steel. Die cast aluminum can be processed and its properties can be altered through processes such as pressure casting, heat treatment, and surface treatment. Stainless steel can be processed and its shape and properties can be changed through processes such as cold working, hot working, and welding.
4. Usage scenarios
Due to its high strength and corrosion resistance, die cast aluminum has been widely used in fields such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Stainless steel is mainly used in kitchenware, medical equipment, building materials and other fields, and its corrosion resistance and aesthetic performance are one of the reasons for its wide application.

